Firstly it’s necessary to understand which are Tomcat and Web Sphere
Tomcat and IBM WebSphere are both HTTP Java servers
Server: is a machine always on, which serves the client requests: the client asks for a request the server processes it and replies with a response.
HTTP is the Hyper Text transfer protocol, it’s a request- response protocol for exchanging web pages.
A Java HTTP web server is a HTTP server which has a JVM (Java virtual machine) which allows to execute Java web applications.
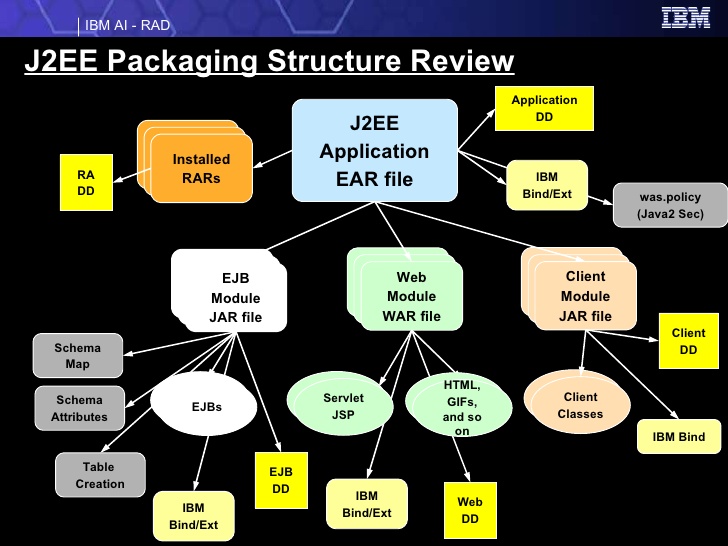
A java web application can be stored in two archives: War and EAR.
- WAR or web archive is an archive made of the below structure:
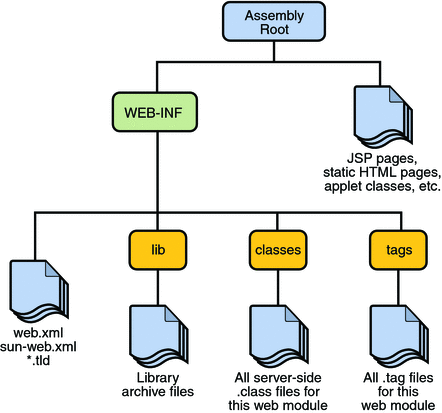
- this archive is made of the below files
- web.xml is the application descriptors which contains the configuration information of the application
- lib: is a folder with all jar files necessary to make working our project
- classes: all project byte codes
- JSP: the Java server Pages which contain html, css javascript code and Java code as well. After the user clicks on the button it may execute the java code inside the JSP or can call a class stored in the “classes folder” which can use a jar file contained in the lib folder.
- this archive can be made in many ways
- using the eclipse export tool: export as->war
- using the Java building tools such as Ant, Maven, Gradle
- EAR entreprise Archive is a more complex archive which can contain more war and the EJB JAR. The EJB or Enterprise Java Beans are necessary for implementing the session, the persistence of data and the message queue. EJB are used by Java front end framework such as JSF and Struts. If using Spring it has their own beans and it can make the above functions without needing EJB
After having clear the function about a Java web application and a java web server we can compare Tomcat and WebSphere
- Tomcat: freeware open source server that is light and fast it doesn’t have a EJB container and it allows only to deploy EAR applications
- Web Sphere: Private IBM server very complex and expensive with the EJB container and the opportunity to install war and ear files. WebSphere allows to use JNDI, Queues and many other technologies.
Both servers work with the java web applications (war) with JSP, Class files but being more widely supported Web Sphere is used for complex projects such as banks and insurances rather then Tomcat used for small projects such as web sites and small applications.